Subsurface Solutions

Project Topics
Reservoir Simulation Research program (SUPRI-B)

SUPRI-B is dedicated to research and development of advanced numerical techniques that enhance the value of reservoir simulation technology. Educating and developing the future leaders in the broad field of reservoir simulation and the wider energy industry are integral to the SUPRI-B mission.
Smart Fields Consortium

Our aim is to develop efficient software tools for the optimization of oil field development and operations. This includes data assimilation, fast simulation, model updating, and optimal control. Techniques being developed by our group are essential for the success of Smart Fields, also known in by names such as i-fields, e-fields, Field of the Future, etc. Optimal control can be implemented in existing fields at any stage of their development and in new fields. We have demonstrated that traditional approaches for developing and operating oil and gas fields are rarely optimal. The positional gains of deploying these new technologies are very significant.
Stress and Crustal Mechanics Group
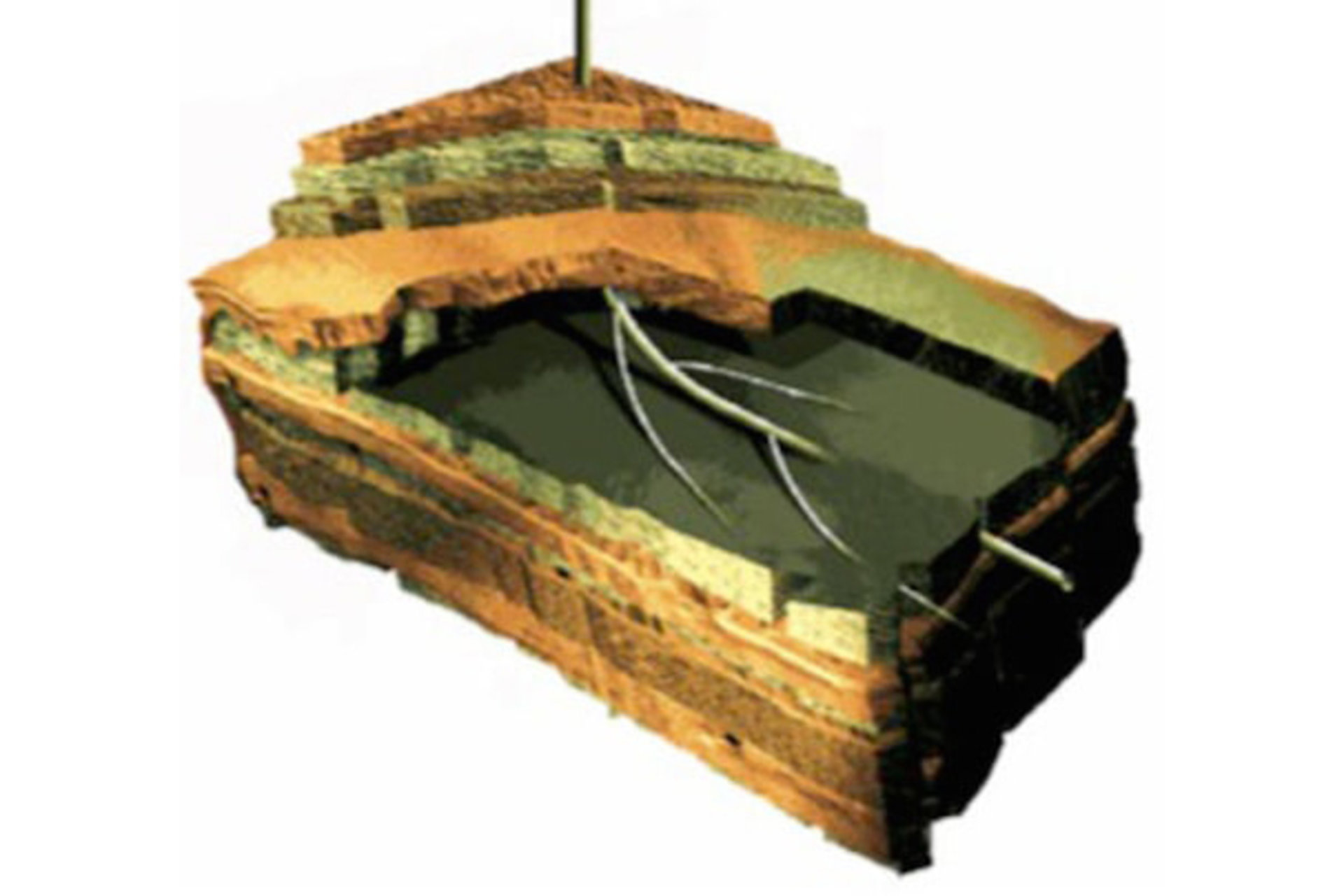

The Stress and Crustal Mechanics Group uses knowledge of the state of stress in the Earth and the mechanical properties of Earth materials to investigate a variety of geophysical problems. These problems cover a variety of scales, ranging from pore-scale processes and the mechanical behavior of reservoir-scale to the strength of the lithosphere and the mechanics of major plate-bounding faults such as the San Andreas. Our group conducts basic and applied research in the areas of reservoir geomechanics, and the physics of friction and faulting. We treat the Earth's crust as a natural laboratory, using a combination of stress and strain data obtained from boreholes, GPS measurements, and earthquake focal mechanisms to test theories about the behavior of the lithosphere. Our group is heavily engaged in applying these methodologies toward optimization of production from gas shale research and CO2 sequestration.
Stanford Center for Earth Resources Forecasting (SCERF)

SCERF provides research in the exploration, evaluation & development of Earth Resources, whether Energy, Water or Minerals. Its mission is to provide solutions for such problems from data acquisition to decision analysis. We focus on developing state-of-the-art data scientific methods for the integration of spatial data over many scales, the quantification of uncertainty of subsurface systems, the value of information of data sources in the context of decision-making purposes.








Find Courses
- Crustal Mechanics
GEOPHYS 385K (Aut, Win, Spr, Sum) - Earthquake Seismology, Deformation, and Stress
GEOPHYS 385L (Aut, Spr, Sum) - Radio Remote Sensing
GEOPHYS 385Z (Sum) - Reservoir Geomechanics
GEOPHYS 202 (Win) - Unconventional Reservoir Geomechanics
GEOPHYS 208 (Spr) - Energy and the Environment
EARTHSYS 101, ENERGY 101 (Win) - Fundamentals of Energy Processes
EE 293B, ENERGY 293B (Win) - Thermodynamics of Equilibria
ENERGY 251 (Aut) - Advanced Reservoir Engineering
ENERGY 222 (Spr) - Advanced Reservoir Simulation
ENERGY 224 (Aut) - Reservoir Simulation
ENERGY 223 (Win) - Fundamentals of Multiphase Flow
ENERGY 121, ENERGY 221 (Win) - The Petroleum System: Investigative method to explore for conventional & unconventional hydrocarbons
GEOLSCI 248 (Aut) - Seismic Reservoir Characterization
ENERGY 141, ENERGY 241, GEOPHYS 241A (Spr) - Fundamentals of Petroleum Engineering
ENERGY 120, ENGR 120 (Aut) - Quantifying Uncertainty in Subsurface Systems
GEOLSCI 260 (Spr) - Exploring Geosciences with MATLAB
ENERGY 112, GEOPHYS 112 (Aut)
Related Publications
- Zoback, Mark, and Dirk Smit. “Meeting the Challenges of Large-Scale Carbon Storage and Hydrogen Production”, PNAS, 120, no. 11 (March 6, 2023). https://doi.org/doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202397120.
- Shi, L, KJ Mach, S Suh, and A Brandt. “Functionality-Based Life Cycle Assessment Framework: An Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) Product Case Study”, Wiley, 19.
- Orsini, Rachel, Philip Brodrick, Adam Brandt, and Louis Durlofsky. “Computational Optimization of Solar Thermal Generation With Energy Storage”, Elsevier, 47 (October 2021): 101342.
- Nie, Yuhao, Ahmed Zamzam, and Adam Brandt. “Resampling and Data Augmentation for Short-Term PV Output Prediction Based on an Imbalanced Sky Images Dataset Using Convolutional Neural Networks”, Pergamon, 224 (August 2021): 341-54.
- Mukerji, Vishal Das Ahinoam Pollack Uri Wollner And Tapan. “Convolutional Neural Network for Seismic Impedance Inversion”.
- Rostami, Erfan, Naomi Boness, and Mark Zoback. “Significance of Well Orientation on Cumulative Production From Wells in the Bakken Region”.
- G., Mavko, Mukerji T., and Dvorkin J. The Rock Physics Handbook, 3rd Ed..
- K., Fossum Ryan Mukerji Eidsvik Maughan Ludvigsen Rajan. “Compact Models for Adaptive Sampling in Marine Robotics”.
- R., Vega Yang Tchelepi Kovscek. “Investigation of Stress Field and Fracture Development During Shale Maturation Using Analog Rock Systems”.
- J., Dutta Mukerji Eidsvik. “Value of Information Analysis for Subsurface Energy Resources Applications”.
- A., Wong Kwok Horne Tchelepi. “Sequential-Implicit Newton Method for Multiphysics Simulation”.
- G., Al Ibrahim Kerimov Mukerji Mavko. “Particula: A Simulator Tool for Computational Rock Physics of Granular Media”.
- Teichgraeber, Holger, and Adam R.Brandt. “Clustering Methods to Find Representative Periods for the Optimization of Energy Systems: An Initial Framework and Comparison”, Applied Energy.
- R., Kim Kovscek. “The Effect of Voidage-Displacement Ratio on Critical Gas Saturation”.